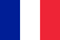
Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland. Currently, urologists are inclined to believe that prostatitis is not a single disease, but combines several diseases of the male genital area. This is one of the most common pathologies of the male urogenital tract and according to experts, the percentage of men suffering from prostatitis in one form or another is constantly increasing. With age, the risk of developing prostatitis increases.
Causes of prostatitis
The immediate cause of prostatitis are two factors of equal importance. The first is the appearance of congestion in the small pelvis and consequently in the prostate and the second the addition of an infection. However, in some cases, it is not possible to detect an infectious agent in prostate tissue, apparently in such cases, autoimmune processes become the cause of prostatitis, which means that the prostate gland is attacked by its immune cells. system, as a result of a malfunction in it.
Predisposing factors for the onset of inflammation in the prostate gland are: weakening of the immune system as a result of an infection, hypothermia, stress; hormonal disorders, incomplete ejaculation, physical inactivity, food preference (dependence on fried, fatty, smoked, spicy foods), frequent urination. Irregular sex life is considered to be one of the common causes of prostatitis.
Types of prostatitis
Currently, the international classification of prostatitis has been adopted, which is the most complete and covers all types of inflammation:
- Category I. Acute prostatitis;
- Category II. Chronic bacterial prostatitis;
- Category III. Chronic nonbacterial prostatitis / Chronic pelvic pain syndrome - a disease in which no infection lasting more than 3 months is detected;
- Subcategory III A. Chronic pelvic inflammatory pain syndrome (leukocytes are defined in prostate secretion);
- Subcategory III B. Chronic non-inflammatory pelvic pain syndrome (no leukocytes in prostate secretion);
- Category IV. Chronic asymptomatic prostatitis (leukocytes are present in the secretion of the prostate, the patient presents no complaints, the disease is detected by chance).
- pain in the genital area and pelvis;
- urinary disorders, which include slow flow, intermittent current, incomplete emptying of the bladder, frequent urination, etc. ;
- disorders in the genital area.
- prostate gland secretion analysis;
- digital rectal examination;
- transrectal ultrasound of the prostate;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder;
- a blood test for PSA (prostate antigen);
- general blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- urine analysis for urogenital infections before and after prostate massage;
- uroflowmetry (urine test).
Symptoms of prostatitis
There is the so-called "prostate triad", the three most common symptoms of prostatitis. This includes:
It should be noted that not all three symptoms of prostatitis are mandatory, in addition, acute and chronic prostatitis persist in different ways.
Symptoms of acute prostatitis: severe, sharp pain in the area of the prostate gland, which is given to the rectum, perineum, testicles, back; deterioration of general condition, fever, headache and muscle aches, general weakness; violation of urination to acute retention of urine as a result of prostate edema and urethral compression.
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis: pain in the prostate gland area, but less intense than in acute prostate; urinary disorders, sexual disorders: incomplete erection, short-term erection, accelerated ejaculation, etc. Chronic prostatitis may have a wavy course, when periods of deterioration are replaced by periods of decline, or there may be mild persistent symptoms.
Unlike other inflammatory diseases, when a chronic process is a consequence of untreated acute inflammation, chronic prostatitis is often chronic primary, when the patient himself finds it difficult to determine the onset of the disease.
Diagnosis of prostatitis
To diagnose prostatitis, the following studies are performed:
The main thing in diagnosis is to identify the cause of prostatitis, as therapeutic measures depend on it. Another diagnostic challenge is the exclusion of prostate cancer.
Treatment of prostatitis
Acute and chronic prostatitis of bacterial origin is treated with antibacterial drugs. For acute prostatitis, strong doses of antibiotics are prescribed even before the results of the bacterial culture are obtained, as the acute process requires immediate measures. In the complex, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, which also have an analgesic effect.
Chronic prostatitis is treated depending on the underlying cause. For non-bacterial prostatitis, general strengthening, immunomodulatory drugs are taken. Treatment of prostatitis is performed with the mandatory participation of physiotherapeutic procedures: laser therapy, magnetotherapy, electrophoresis of medicinal substances, ultrasound, etc.
Urologists say that treating prostatitis only with medical means will bring only temporary relief, as without changing the usual lifestyle, treating prostatitis is ineffective. It is necessary to give up bad habits, lead an active lifestyle, eliminate hypodynamics, avoid getting stuck in the small pelvis with the help of special gymnastics, try to spend less time in the car, walk more andalso have enough rest.
It is also important to improve your sex life by making it regular and eating well. Chronic prostatitis is prone to relapse, so lifestyle changes should be permanent, only in this case, treatment of prostatitis will lead to a complete cure.
Treatment of prostatitis with folk remedies
Popular methods are widely and successfully used to treat prostatitis, especially for the treatment of chronic prostatitis. They act milder than medications, but are nevertheless quite effective and give fewer side effects, so that the treatment of prostatitis with folk remedies is carried out for a long time, until the symptoms of the disease are eliminated.
Among the popular remedies for the treatment of prostatitis, teas prepared from medicinal herbs with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects are widely used: tea made from chamomile, sage leaves, calendula flowers, etc. Medicinal plants are also used in the form of tinctures and balms. Honey and bee products are used as tonic agents. Beeswax is perfect for wrapping in the treatment of chronic prostatitis, replacing paraffin wax. Echinacea tincture is used as a mild immunostimulatory agent; for the same purpose, several types of honey are used successfully.